 ISO 24444 / ISO 24443
ISO 24444 / ISO 24443 EU COLIPA and SANS 1557 Verified Broadspectrum Sunscreens

UV (Ultra-Violet) rays are invisible radiation emitted by the sun. There are three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC, each with different wavelengths and effects on human skin. Understanding these rays is essential for proper sun protection.
UVA is the most abundant form of UV radiation that reaches the earth's surface. This radiation can:
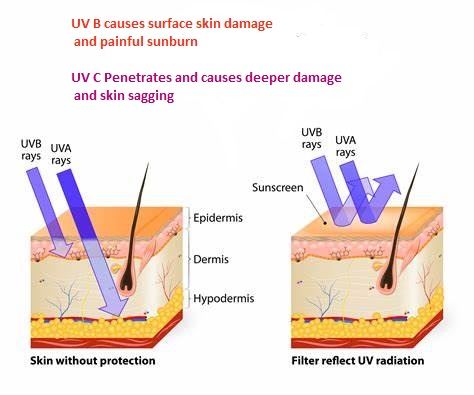
UVB radiation affects the outer layer of skin (epidermis) and:
UVC is the most dangerous type of UV radiation, but fortunately:
Different UV wavelengths penetrate the skin to different depths. UVA rays reach deeper into the skin than UVB, causing damage to the connective tissue and potentially leading to long-term issues including skin cancer.
UV rays can also reflect off surfaces like sand, concrete, water, and especially snow, increasing your exposure. This is why sun protection is crucial even when you're not in direct sunlight.
Research has shown that just one severe sunburn in childhood or adolescence more than doubles the risk of developing melanoma later in life. Sunburns cause immediate damage visible as redness and pain, but the long-term DNA damage can emerge years or decades later.

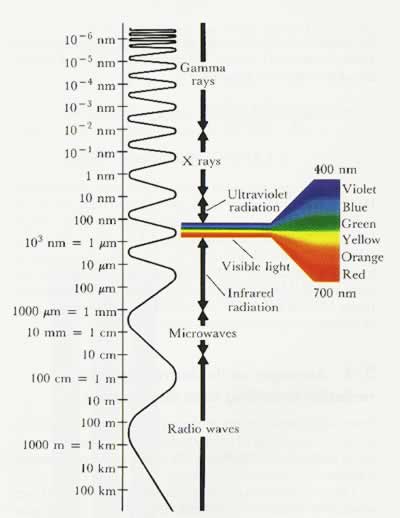
UV radiation is just a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that reaches Earth. It sits just beyond the visible light spectrum that we can see with our eyes.
Below the visible light spectrum is infrared radiation, which we feel as heat. While we can feel infrared and see visible light, UV radiation is invisible but still actively absorbed by our skin cells.
This UV energy absorption can damage skin cell DNA, leading to mutations and potentially skin cancer, which is now the most common form of cancer worldwide.
Kool-a-Sun offers a complete range of sun protection products that guard against harmful UVA and UVB rays. Our formulations are developed to provide effective, long-lasting protection for all skin types and activities.