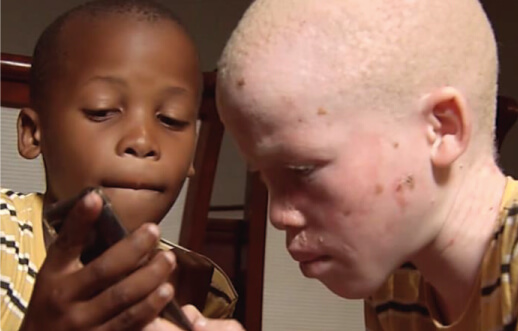
 ISO 24444 / ISO 24443
ISO 24444 / ISO 24443 EU COLIPA and SANS 1557 Verified Broadspectrum Sunscreens

Finding the right balance between sun protection and beneficial sun exposure is key to optimal health. While excessive sun exposure can lead to skin damage and cancer, limited, controlled sun exposure provides essential health benefits, primarily through the production of Vitamin D—often called the "sunshine vitamin."
Vitamin D is one of the most beneficial effects of exposure to sunlight. Our bodies use UVB radiation (290-315 nm wavelength) to manufacture Vitamin D from a form of cholesterol in our skin. While many skin ailments and fungal infections can be managed with sun exposure, Vitamin D production is arguably the sun's most important contribution to our health in modern life.
Vitamin D deficiency has long been known to cause serious bone-related conditions including:

In recent years, numerous research studies1 have shown that inadequate amounts of Vitamin D are suspected to contribute to or increase the risk of the following health conditions:
This creates a challenging situation: any sunscreen or sunblock endorsed by dermatologists (SPF 15 or higher) will block approximately 95% of our skin's ability to produce Vitamin D. Too much sun exposure can cause skin cancer, while too little can lead to Vitamin D deficiency with its own host of health problems.
In some Western countries, 50% of the population over age 50 is reported to have Vitamin D deficiency. The optimal approach is not necessarily to take expensive Vitamin D supplements (where absorption of manufactured Vitamin D varies from person to person), but to safely expose yourself to the sun for short periods without causing permanent skin damage.
The amount of Vitamin D produced from sun exposure varies from person to person. Generally, those with lighter skin tones produce higher amounts of Vitamin D from sunlight exposure.
Key Takeaway: You don't have to overexpose yourself to the sun to get the benefits of natural Vitamin D production. Brief, regular sun exposure without sunscreen, followed by proper sun protection, offers the best balance for most people.
At Kool-a-Sun, we believe in a balanced approach to sun exposure that allows you to benefit from the sun's health advantages while minimizing the risks of skin damage:
Our range of sun protection products allows you to enjoy the benefits of vitamin D production while protecting against harmful overexposure. Contact our skin health specialists to discuss your specific needs:
View Our Balanced Sun Protection Products Learn About UV Radiation